
HOME
Harmonist Structures
After the Harmonists
Harmonist Society
Other Links
IUPUI Max Kade German American Center
Historic New Harmony's
Official
Web site
http://www.
newharmony
.org
or
http://www.
newharmonyinfo
.com
University of Southern Indiana
New Harmony Scientists, Educators, Writers & Artists
Harmony Museum,
Harmony, PA, 1st Settlement of the Harmonie Society
Old Economy Village, 3rd Settlement of the Harmonie Society

Historic New Harmony, Indiana
 New Harmony is the site of two of America's great utopian communities. The first, Harmonie on the Wabash (1814-1824), was founded by the Harmony Society, a group of Separatists from the German Lutheran Church. In 1814, led by their charismatic leader Johann Georg Rapp, they left their first American home, Harmonie, PA. Indiana's lower Wabash Valley on the western frontier gave them the opportunity to acquire a much larger tract of land. In 1825, the Ha
rmonists moved back to Pennsylvania and built the town of Economy near Pittsburgh. Robert Owen, Welsh-born industrialist and social philosopher, bought their Indiana town and the surrounding lands for his communitarian exper
iment.
New Harmony is the site of two of America's great utopian communities. The first, Harmonie on the Wabash (1814-1824), was founded by the Harmony Society, a group of Separatists from the German Lutheran Church. In 1814, led by their charismatic leader Johann Georg Rapp, they left their first American home, Harmonie, PA. Indiana's lower Wabash Valley on the western frontier gave them the opportunity to acquire a much larger tract of land. In 1825, the Ha
rmonists moved back to Pennsylvania and built the town of Economy near Pittsburgh. Robert Owen, Welsh-born industrialist and social philosopher, bought their Indiana town and the surrounding lands for his communitarian exper
iment.The Harmonists combined the Swabian work ethic ("Work, work, work! Save, save, save!") with the Benedictine rule ("Pray and work!"). This resulted in an unheard of economic achievement that was recognized as "the wonder of the west."
How visitors reacted to the Harmonists' holy experiment:
"The settlement made more rapid advances in wealth and prosperity, than any equal body of men in the world at any period of time, more, in one year, than other parts of the United States ... have done in ten."
- Matthew Carey
"But whether reverend Rapp learned this while in Germany
Or no, 'it is said his sect is rich and godly,
Pious and pure, beyond what I can term any
Of ours, although they propagate more broadly."
- Lord Byron
"Niemals habe ich eine so wahrhaft patriarchalische Verfassung gesehen als hier, und das, was die Menschen gewirkt haben, spricht am Besten fü:r ihre Einrichtungen und für die unter ihnen herrschende Eintracht."The focus of this Website is primarily on the German sites and buildings and Harmonist history. Eight Harmonist sites and 25 Harmonist buildings are identifiable today in central New Harmony. Some of these are a part of tours, others are privately owned.
- Duke Bernhard of Weimar
By standing under the town's only traffic light at the intersection of Main and Church Streets and looking around, one can see all of New Harmony. It is still a small town, just shy of 1,000 people, and with lots of historical reminders.
 The town is a vacationer's dream and a researcher's paradise, with
12 early 19th century buildings and 20 from mid-19th century, a museum,
library, gallery and a theater. The New Harmony Inn with its Conference
Center, a unique assemblage of contemporary buildings within the context of
the historic community, offers the comforts of city-living in a rural setting.
Visitors from all over the world come to experience New Harmony's legacy of
creative endeavor which has spanned more than 180 years. They discover a
distinctive small town, where the simple wooden structures of the Harmonists,
blend with modern architectural masterpieces on quiet tree-lined streets.
The town is a vacationer's dream and a researcher's paradise, with
12 early 19th century buildings and 20 from mid-19th century, a museum,
library, gallery and a theater. The New Harmony Inn with its Conference
Center, a unique assemblage of contemporary buildings within the context of
the historic community, offers the comforts of city-living in a rural setting.
Visitors from all over the world come to experience New Harmony's legacy of
creative endeavor which has spanned more than 180 years. They discover a
distinctive small town, where the simple wooden structures of the Harmonists,
blend with modern architectural masterpieces on quiet tree-lined streets.
 Historic restorations are not unusual, nor is community development. Why
then, is this small town in southern Indiana of such importance? New Harmony
has acted early to secure control in the public interest over substantial
parts of its central Historic District. It is a village museum and
preservation project, and it has been a center for culture and learning
ever since its beginnings.
Historic restorations are not unusual, nor is community development. Why
then, is this small town in southern Indiana of such importance? New Harmony
has acted early to secure control in the public interest over substantial
parts of its central Historic District. It is a village museum and
preservation project, and it has been a center for culture and learning
ever since its beginnings.
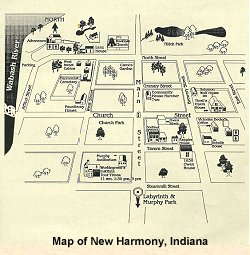
The town's unique history comes alive on guided tours offered to 15 historic sites. Some of these include period rooms and other exhibits relating to specific subjects. The guided tours begin at the Atheneum/Visitor Center.
The Harmony Society established a remarkably well-planned town on the Indiana Frontier. This deeply religious communitarian group had come from Württemberg, Germany to Pennsylvania in 1804 and relocated to the Indiana territory in 1814. In January 1825 they sold the entire town to Robert Owen of New Lanark, Scotland. By May all the Harmonists had departed for Pennsylvania, where they established their third and final settlement. Old Economy is today a National Historic Landmark village of 17 restored 1824-1830 structures and recreated 1824 gardens. 16,000 objects are exhibited there.
 The Indiana years proved to be the golden decade of the Harmony society.
Their industries prospered. Agricultural and manufactured products were
marketed to major cities in the United States and abroad. New Harmony, with
it manicured gardens and neat tree-lined street, was renowned for its
beauty. The town was largely self-sufficient. There were 2000 acres of
highly cultivated land, including a 15-acre vineyard and a 35-acre orchard
of choice apple and pear tress. Four large brick dwellings, a steam engine,
two large granaries, wool and cotton factories, a threshing machine, a
5-acre vegetable garden, and more than 126 family dwelling houses were
carefully cataloged by the Harmonists in a final inventory of the town that
was prepared prior to its sale to Robert Owen.
The Indiana years proved to be the golden decade of the Harmony society.
Their industries prospered. Agricultural and manufactured products were
marketed to major cities in the United States and abroad. New Harmony, with
it manicured gardens and neat tree-lined street, was renowned for its
beauty. The town was largely self-sufficient. There were 2000 acres of
highly cultivated land, including a 15-acre vineyard and a 35-acre orchard
of choice apple and pear tress. Four large brick dwellings, a steam engine,
two large granaries, wool and cotton factories, a threshing machine, a
5-acre vegetable garden, and more than 126 family dwelling houses were
carefully cataloged by the Harmonists in a final inventory of the town that
was prepared prior to its sale to Robert Owen.
Robert Owen's ambition was to create a more perfect society through free education and the abolition of social classes and personal wealth. World-renowned scientists and educators settled in New Harmony. With the help of William Maclure, the Scottish geologist and businessman, they introduced vocation education, kindergarten and other educational reforms.
New Harmony is also the site of the early headquarters of the U.S. Geological Survey and provided the earliest geological and natural science collections for the beginnings of the Smithsonian Institute. David Dale Owen turned to geology under the influence of William Maclure. From 1830 until 1860 New Harmony was one of the most important training and research centers for the study of geology in America. Historic New Harmony is a Unified Program of the University of Southern Indiana and the Division of Indiana State Museums & Historic Sites.
Historic New Harmony, Inc.
Connie Weinzapfel, Director
P.O. Box 579, New Harmony, IN 47631
For information: 1-800-231-2168
E-mail: harmony@usi.edu
URL: http://www.newharmony.org
Hours: March 15-December 30, daily 9 a.m.-5 p.m.
Other times, call for hours.
The site had been surveyed by the Historic American Building Survey and has been placed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1966.
The historic site consists of many Harmonist (1814-1824) and later 19th century buildings. Gardens and a reconstructed Harmonist Labyrinth can be seen in town. Although there are still many Harmonist buildings, much of Historic New Harmony's collection relates to the Owen community and later periods of New Harmony history. Some archival material and artifacts relate to the Harmony Society.
Time Periods from which buildings/artifacts originate:
1814-1824 Harmonist
1825-1827 Owen-Maclure
1827-1860 Post Communal
The most relevant German-American collections are:
Maximilian-Bodmer Print Collection, 1832-34
Harmony Society reproduction furniture and pottery, 1814-1824
Jacob Maentel (1778-1863) drawings and paintings
Return to Top of Page
|
Created: 21 September 1998, JAF Supported by an Indiana Heritage Research Grant, A Joint Effort of the Indiana Humanities Council and the Indiana Historical Society Updated: 17 November 2007, BAS Indiana University Purdue University Indianapolis, University Library URL: http://www.ulib.iupui.edu/kade/newharmony/ Comments: Ruth Reichmann, reichman@indiana.edu |

IUPUI School of Liberal Arts |

IUPUI University Library |
IUPUI Home Page |